
K Nearest Neighbour (KNN) from scratch
Matlab project.
KNN is a learning algorithm which can be used for classification. The output is classified by a majority vote of its neighbors.
GitHub link: https://github.com/Apiquet/KNN_algorithm
As it’s always easier to understand through an example, let’s see the following one:

The classification is determined by K. It represents the number of neighbors to take to classify the new object. It will take the class the most present among the K neighbors. As I wrote on my example, if K=1 the new object would be classified as a class 1 object, if K=5 it would be a class 2 object.
How to implement a KNN algorithm on Matlab?
We need to obtain data and labels corresponding to that data. Let’s take a simple example to start with: a data matrix of M_training samples, each of dimension N (matrix dimension: N x M_train). Then a vector with labels 1 or 2 corresponding to the M_training samples (dimension 1 x M_train). These two matrices are for learning, we need another one for testing: let’s take a matrix of M_test samples of dimension N (matrix dimension: N x M_test).
First, we need to declare and calculate a matrix which represents the distance between each training and test samples. For that we just need to calculate the norm between each sample. In other words, we must calculate the norm between the first test sample and the first training sample, then the first test sample and the second training sample,…, the second test sample and the first training sample, etc. We thus get a number per distance calculated so M_test x M_training number. We will store it in a matrix. We simple do two for loop to calculate it:
[N, M_test] = size(X_test);
[~, M_train] = size(X_train);
y_est = zeros(1, M_test);
Matrix_dist = zeros(M_test,M_train);
for i = 1:M_test
for j = 1:M_train
Matrix_dist(i,j) = my_distance(X_test(:,i),X_train(:,j),params);
end
end
My_distance simply does the calculation of the norm 2:
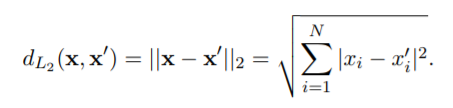
for i=1:N
d=d+(abs(x_1(i)-x_2(i)))^2;
end
To implement the KNN algorithm, we need to remember what we need: getting the K nearest neighbors of each test sample among the training samples. Then, we must calculate the class the most represented among the K nearest training sample to classify the test sample.
To realize this calculation we will use the matrix of distances we calculated above. As it represent the distance between each test sample and each training data we just need to sort it:
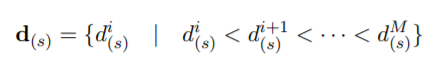
We take the first K distances (we thus get the K smallest distances among all the distances). Then, we extract the corresponding index to get the labels (1 or 2) of these K training samples. Finally, we calculate if the test sample has more “1” or “2” class training around it:
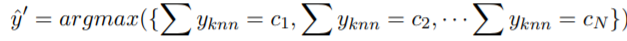
for i = 1:M_test
[sorted_line,k_min_index] = sort(Matrix_dist(i,:));
sorted_line = sorted_line(1:params.k);
k_min_index = k_min_index(1:params.k);
labels=zeros(1,params.k);
for j = 1:params.k
labels(j) = y_train(k_min_index(j));
end
[value,freq] = mode(labels(:));
y_est(i) = value;
end
Accuracy:
To calculate the accuracy, we need to have the class of each test sample to compare with the class we found from our KNN algorithm. The accuracy can be calculate as follow:
N = length(y_test);
count = 0;
for i = 1:N
if(y_test(i)==y_est(i)) count=count+1; end
end
acc = count/N;
Where y_test is the real class and y_est is the class we calculated from the KNN algorithm.
At this point, most of the work is done. We can run our program with several K numbers and compare the accuracy.
Result:
Thanks to plot function we can visualize how our KNN works.
First, let’s see our test samples with its class color: class 1 in red, class 2 in blue.
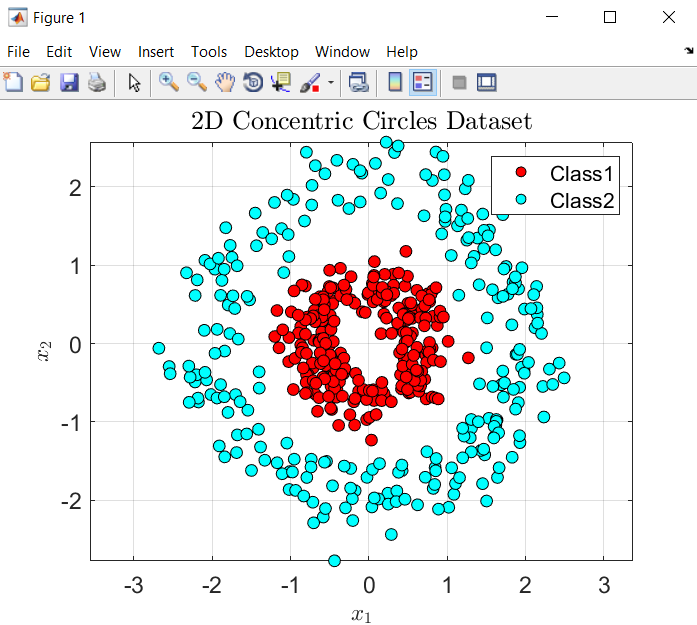
Then, let’s visualize how our KNN algorithm works for K=3 and K=20. I’m displaying a circle around each test sample to know which class was determined by the algorithm:




As expected, the higher the K, the lower the accuracy.
Here you can find the whole code: https://github.com/Apiquet/KNN_algorithm
